Understanding White Matter Tractography
Understanding White Matter Tractography: Visualization and Mapping of Brain Pathways
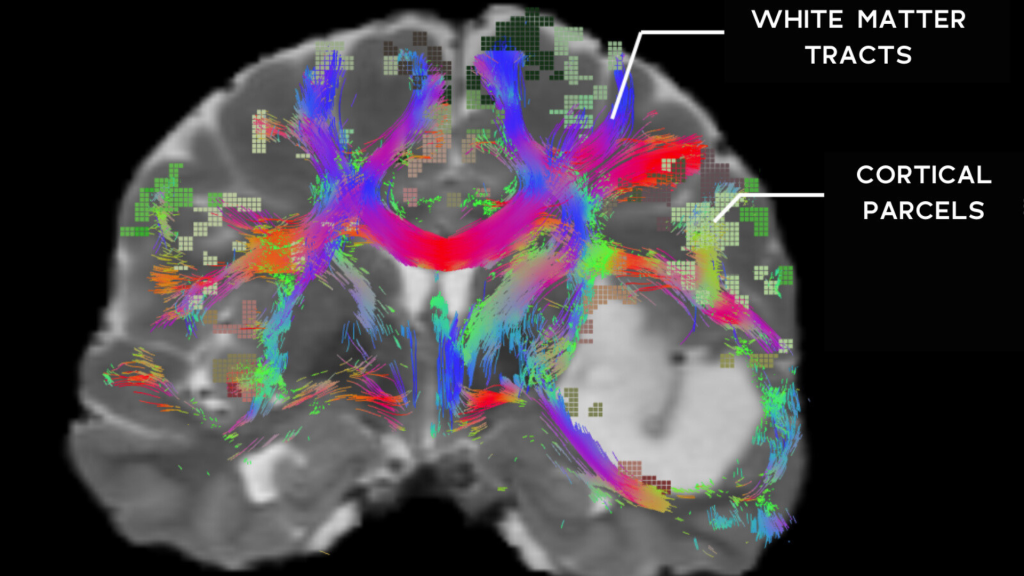
Objective: To understand the principles and applications of white matter tractography using Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) to visualize and map brain pathways.
White matter tractography is a method used to map the neural pathways in the brain, focusing on the white matter. White matter consists of nerve fibers (axons) that connect different regions of the brain, facilitating communication between them. DTI is a powerful imaging technique that allows us to visualize and study these fiber pathways in vivo, providing valuable insights into brain structure and function.
Key Concepts in White Matter Tractography:
Diffusion of Water Molecules:
- Water molecules in the brain diffuse more freely along the direction of the white matter fibers due to the structure of axons.
- DTI measures the direction and extent of this diffusion, which can be used to visualize the orientation of the white matter tracts.
Tensor Representation:
- The diffusion of water molecules is not uniform in all directions. DTI uses a mathematical model called a tensor to describe the diffusion pattern. This tensor provides information about the directionality and the degree of diffusion along each axon, which is critical for mapping white matter tracts.
Tractography Algorithms:
- Algorithms process the DTI data to reconstruct and visualize the white matter tracts. These algorithms trace the direction of diffusion through the brain, generating 3D representations of the pathways.
Applications of White Matter Tractography:
Mapping Brain Pathways:
- By visualizing white matter tracts, researchers and clinicians can identify the major neural pathways such as the corticospinal tract, corpus callosum, and the arcuate fasciculus.
Assessing Brain Function:
- The integrity of these pathways is critical for brain function. Disruptions in white matter tracts can be associated with various neurological conditions, such as stroke, traumatic brain injury (TBI), or neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Real-World Example:
Stroke Rehabilitation:
- In patients recovering from a stroke, DTI is used to track changes in white matter pathways, aiding in the assessment of neural recovery and guiding rehabilitation efforts.
Case Study:
Multiple Sclerosis (MS):
- DTI is used to detect changes in the white matter integrity in MS patients, showing disruptions in the normal brain connectivity that could help understand the disease progression and treatment response.