Key Milestones
- Development of Computed Tomography (CT) Scanning
- Year: 1971
- Developer: Sir Godfrey Hounsfield
- Impact: Revolutionized medical imaging by providing detailed cross-sectional images of the brain. Enabled non-invasive visualization of intracranial structures, improving diagnosis and treatment of tumors, hemorrhages, and structural abnormalities. Marked a significant leap in diagnostic radiology.
2. Introduction of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Year: Early 1970s
- Developers: Paul Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield
- Impact: Utilized magnetic fields and radio waves to produce high-resolution images of brain structures without ionizing radiation. Became a cornerstone in neuroimaging for diagnosing disorders like multiple sclerosis, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases. Advanced clinical neuroscience and research significantly.
Specific Techniques or Discoveries That Have Transformed Neuroscience
1. Discovery of Default Mode Network (DMN) Using fMRI
- Description: The DMN was identified in the late 1990s using resting-state functional MRI (fMRI). It revealed a network of brain regions that are active during rest and introspective activities, such as daydreaming or self-referential thinking.
- Impact: This discovery revolutionized understanding of how the brain operates in a baseline state and its alterations in disorders like Alzheimer’s, schizophrenia, and depression.
2. Application of Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Description: DTI has been instrumental in visualizing white matter damage in TBI patients by tracking water diffusion along neural pathways.
- Impact: This technique has improved diagnosis and rehabilitation strategies by providing detailed insights into structural damage that conventional imaging misses. It has also contributed to understanding connectivity in neural networks.
The Impact of These Advancements on Modern Imaging and Diagnosis:
1. Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
- Description: Advancements such as MRI, fMRI, and DTI have significantly increased the accuracy of diagnosing complex neurological conditions. For example:
- MRI provides high-resolution images of brain structures, enabling early detection of tumors, multiple sclerosis, and stroke.
- fMRI and PET scans offer insights into functional abnormalities, which are critical in diagnosing conditions like epilepsy or psychiatric disorders.
- Impact: Early and accurate diagnosis facilitates timely intervention, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
2. Personalized Treatment Strategies
- Description: Modern imaging techniques provide detailed structural and functional information that aids in tailoring treatments to individual patients. For example:
- Pre-surgical Planning: MRI and DTI help map brain structures and connectivity, minimizing risks during neurosurgery.
- Therapeutic Monitoring: PET scans track metabolic changes, assessing the effectiveness of treatments like chemotherapy or neurostimulation.
- Impact: These advancements have ushered in an era of personalized medicine, optimizing therapeutic outcomes and reducing side effects.
3. Enhanced Understanding of Neurological Disorders
- Description: Modern neuroimaging has deepened understanding of disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and schizophrenia by identifying biomarkers and tracking disease progression.
- Impact: This knowledge has driven the development of targeted therapies and improved prognostic tools, transforming the landscape of neurological care.
Real-World Examples
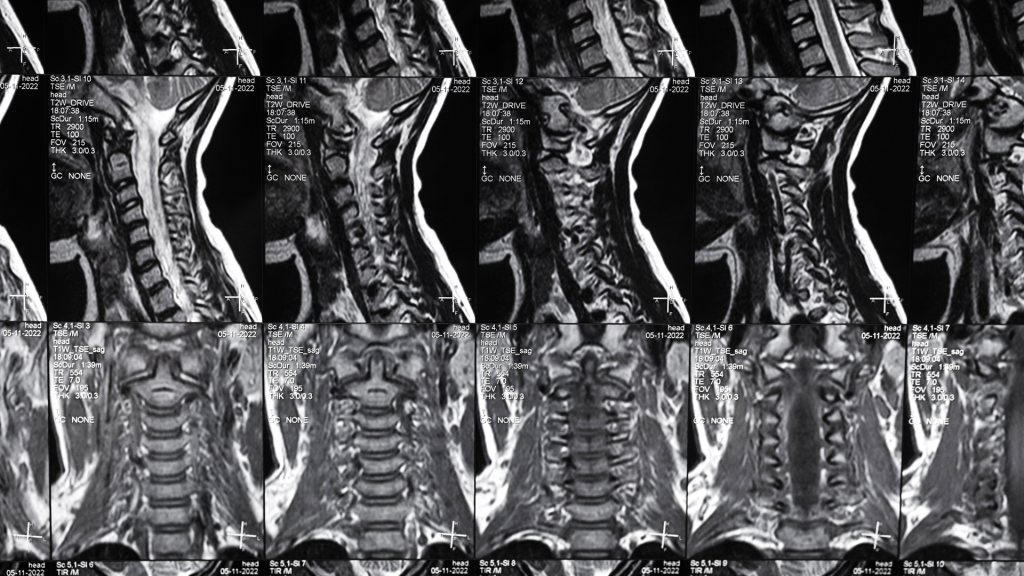
1. Early Detection of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Using MRI
- Case Study: A patient presenting with a clinically isolated syndrome underwent MRI, revealing demyelinating lesions indicative of MS. This early detection allowed for prompt initiation of disease-modifying therapies, potentially altering the disease course.
Read the full article here.
2. Localization of Epileptic Seizure Focus with fMRI
- Case Study: In a pre-surgical evaluation, fMRI was utilized to identify the epileptic focus in a patient with refractory epilepsy. This precise localization informed surgical planning, leading to successful resection of the seizure focus and significant reduction in seizure frequency.
Read the full article here.